Lock and Key Enzyme
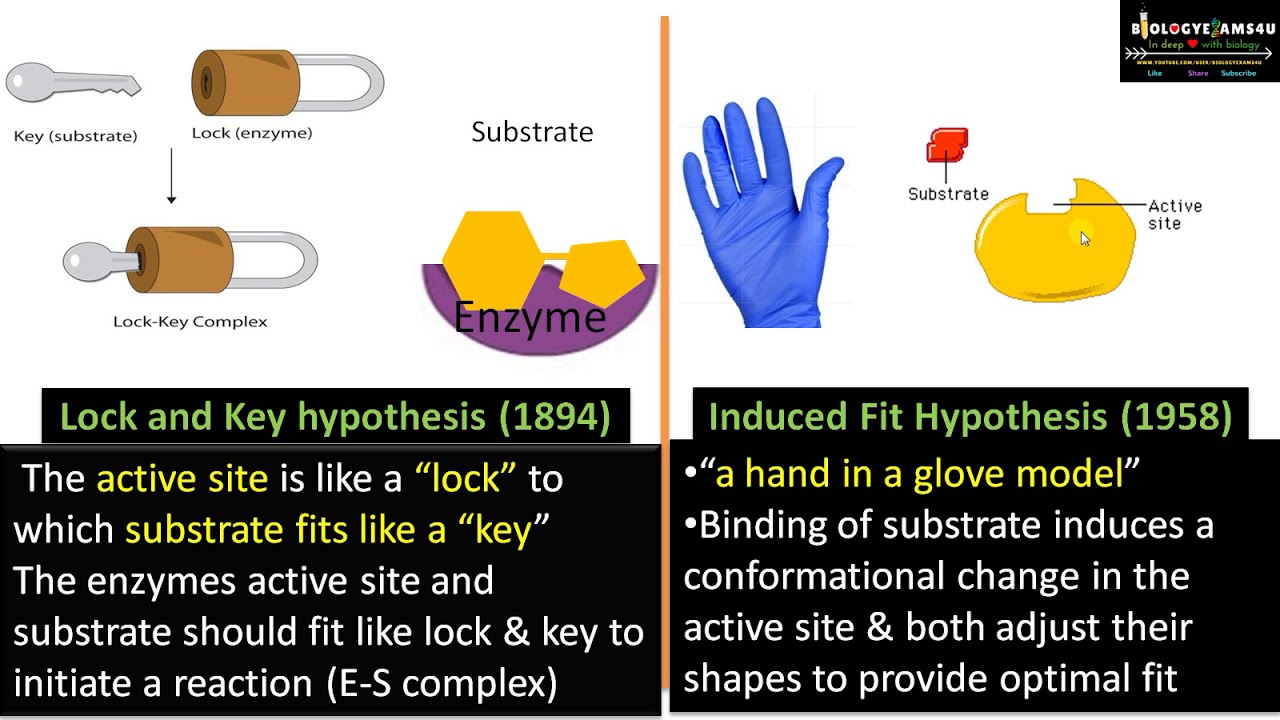
The enzyme-substrate interaction in the lock-and-key paradigm implies that the enzyme and the substrate have complimentary geometric forms that fit perfectly together. Only one key can open the lock correctly.
Difference Between Lock And Key Hypothesis And Induced Fit Hypothesis Choice Questions Multiple Choice Lock And Key
Lock and key hypothesis have a simple approach which says that the particular substrate perfectly fits into the enzymes cleft active site for the reaction to occur.

. Consider checking renal function in patients with suspected renal impairment. Enzymes are denatured at extremes of temperature and pH. According to the induced fit model proposed by.
All outer and inner surfaces of the human body a key part of the innate immune system. Some cofactors are required to produce a chemical reaction between the enzyme and the substrate while others merely increase the rate of catalysis. Apart from active sites enzymes have allosteric sites or inhibitor sitesInhibitors may join an enzyme at an active site or allosteric site.
And the active site of an enzyme. Only the right size and form of the substrate the key would fit into the active site the key hole of the enzyme similar to a key into a lock the lock. Cofactors are sometimes attach to the enzyme much like a prosthetic limb.
Cofactors are inorganic substrates. The lock and key hypothesis models this. In many cases however the configurations of both the enzyme and substrate are modified by substrate bindinga process called induced fit.
Before prescribing RTV-boosted nirmatrelvir carefully review concomitant medications including OTC. A The lock and key model in this model the substrate has a shape matching the enzymes active site see figure 2 Figure 2 b The induced fit model the active site has a shape complementary to that of the. The active site is where the enzyme reacts and can only act on one substrate which can be other proteins or sugars.
Similarly only one. The simplest model of enzyme-substrate interaction is the lock-and-key model in which the substrate fits precisely into the active site Figure 224. The interaction between the enzyme and the substrate is rather static and rigid as opposed to the more flexible interaction depicted by the induced fit model.
The docking process in which substrate is put into the active site like a key into a lock then allowed the team to. Liver enzyme abnormalities or hepatitis. The closed surface of the skin and of all mucous membranes already forms a physical barrier against germs which protects them from entering.
Others are loosely bound to the enzyme. The enzyme binds specifically only to a substrate that is an exact fit and only with such high specificity that the enzyme catalyzes the reaction. Cofactors are usually vitamins consumed by various food sources and open the active site on the enzyme.
Enzyme and its Active Site. Similarly the way one specific key fits into the notch of a lock and unlocks it. Cofactors and Enzyme Activity.
Lock and key model. A good way to think about this is to lock and key models. Two explanations of how enzymes interact with substrates are the lock and key model proposed by Emil Fischer in 1894 and the induced fit model which is a modification of the lock and key model that was proposed by Daniel Koshland in 1958In the lock and key model the enzyme and the substrate have three-dimensional shapes that fit each other.
Enzymes are denatured at extremes of temperature and pH. Secure gov websites use HTTPS A lock A locked padlock or https. Additionally chemical substances like acid enzymes or mucus prevent bacteria and viruses from gaining a foothold.
The binding of inhibitors to allosteric sites modifies the structure of the active site thus preventing the binding of substrate to the enzymeThis process is called allostery or allosteric. In such cases the conformation of the substrate is. This latter molecule is known to bind to the enzyme and inhibit its activity.
The amino acid residues enable the enzymes active site to bind specifically with the. RTV-boosted nirmatrelvir has significant drug-drug interactions.

Lock And Key Model Is Used To Describe The Mechanism Of Enzyme Action This Model Was First Proposed By German Chemist Emi Lock And Key Active Site Biochemical

Lock And Key Model Of Enzyme Algebra Worksheets Enzymes Lock And Key

Difference Between Lock And Key Hypothesis And Induced Fit Hypothesis Choice Questions Multiple Choice Lock And Key
No comments for "Lock and Key Enzyme"
Post a Comment